Interact with gRPC Server
A gRPC endpoint is available on the public Osmosis nodes so that you can start playing and intreacting with it right away.
Enabling gRPC on a node
If you are running your own node. It's also possible to enable them by editing ~/.osmosisd/config/app.toml:
grpc.enable = true|falsefield defines if the gRPC server should be enabled. Defaults totrue.grpc.address = {string}field defines the address (really, the port, since the host should be kept at0.0.0.0) the server should bind to. Defaults to0.0.0.0:9090.
Grpc endpoints
An overview of all available gRPC endpoints shipped with Osmosis is available in the Osmosis Protobuf documentation. There is also a Cosmos SDK is Protobuf documentation.
You can send requests to the gRPC server using a gRPC client such as grpcurl or from Buf Studio.
Since the code generation library largely depends on your own tech stack, we will only present three alternatives:
Buf Studio
Interacting with Buf Studio
An interactive web UI for all the gRPC and Protobuf services stored on the Osmosis Buf Schema Registry
Studio preconfigured with the mainnet RPC:
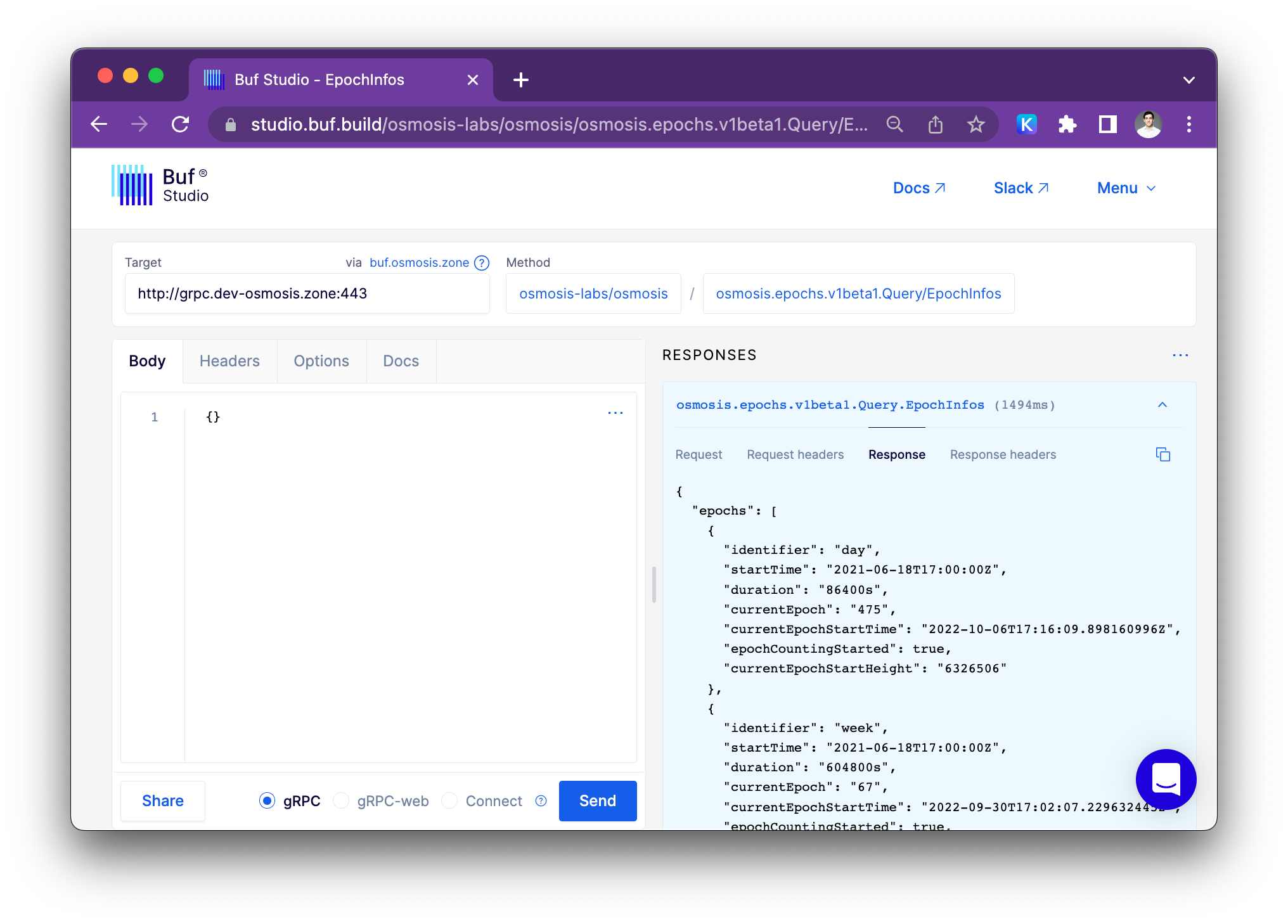
Things you can do with buf Studio:
- Select an endpoint from any BSR module to send requests to gRPC
- Use the editor with schema-based autocompletion, validation and documentation to draft JSON based request messages.
- Configure headers to further customize outgoing requests.
- Optionally include cookies in outgoing request to send authenticated requests to private APIs (or Buf Studio Agent instances).
- Create shareable links for requests defined on Buf Studio to team members with access.
How does buf Studio work with Osmosis
We have a Buf agent running at https://buf.osmosis.zone which will allow you to use the buf data studio to explore the available methods.
gRPCurl
Interacting with grpcurl
grpcurl is like curl but for gRPC. It is also available as a Go library, but we will use it only as a CLI command for debugging and testing purposes. Follow the instructions in the previous link to install it.
Assuming you already installed osmosisd with the installer, you should be able to run the following command to list the Protobuf services available (you can replace grpc.osmosis.zone:9000 by the gRPC server endpoint of another node such as the testnet, another provider or your own node.
Listing all the methods from the mainnet
grpcurl -plaintext grpc.osmosis.zone:9090 list
Output will look like:
cosmos.auth.v1beta1.Query
cosmos.authz.v1beta1.Query
cosmos.bank.v1beta1.Query
cosmos.base.reflection.v1beta1.ReflectionService
cosmos.base.reflection.v2alpha1.ReflectionService
cosmos.base.tendermint.v1beta1.Service
cosmos.distribution.v1beta1.Query
cosmos.evidence.v1beta1.Query
cosmos.gov.v1beta1.Query
cosmos.params.v1beta1.Query
cosmos.slashing.v1beta1.Query
cosmos.staking.v1beta1.Query
cosmos.tx.v1beta1.Service
cosmos.upgrade.v1beta1.Query
cosmwasm.wasm.v1.Query
grpc.reflection.v1alpha.ServerReflection
ibc.applications.interchain_accounts.host.v1.Query
ibc.applications.transfer.v1.Query
ibc.core.channel.v1.Query
ibc.core.client.v1.Query
ibc.core.connection.v1.Query
osmosis.epochs.v1beta1.Query
osmosis.gamm.v1beta1.Query
osmosis.incentives.Query
osmosis.lockup.Query
osmosis.mint.v1beta1.Query
osmosis.poolincentives.v1beta1.Query
osmosis.superfluid.Query
osmosis.tokenfactory.v1beta1.Query
osmosis.twap.v1beta1.Query
osmosis.txfees.v1beta1.Query
testdata.Query
You should see a list of gRPC services, like cosmos.bank.v1beta1.Query. This is called reflection, which is a Protobuf endpoint returning a description of all available endpoints. Each of these represents a different Protobuf service, and each service exposes multiple RPC methods you can query against.
In order to get a description of the service you can run the following command:
grpcurl -plaintext \
grpc.osmosis.zone:9090 \
describe osmosis.gamm.v1beta1.Query
It's also possible to execute an RPC call to query the node for information:
grpcurl -plaintext grpc.dev-osmosis.zone:443 osmosis.gamm.v1beta1.Query.Pools
The list of all available gRPC query endpoints and API exploration is possible with the help of buf studio.
Query for historical state using grpcurl
You may also query for historical data by passing some gRPC metadata to the query: the x-cosmos-block-height metadata should contain the block to query. Using grpcurl as above, the command looks like:
grpcurl \
-plaintext \
-H "x-cosmos-block-height: 6312618" \
-d '{"address":"osmo19a7pmytd9vk26l57q8chacuprsmx05g23mg6yc"}' \
grpc.osmosis.zone:9090 \
cosmos.bank.v1beta1.Query/AllBalances
Note: This endpoint might change to grpc.osmosis.zone:443 in the near future.
Assuming the state at that block has not yet been pruned by the node, this query should return a non-empty response.
Interacting with Go
The following snippet shows how to query the state using gRPC inside a Go program. The idea is to create a gRPC connection, and use the Protobuf-generated client code to query the gRPC server.
Install Cosmos SDK
go get github.com/cosmos/cosmos-sdk@main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"github.com/cosmos/cosmos-sdk/codec"
sdk "github.com/cosmos/cosmos-sdk/types"
banktypes "github.com/cosmos/cosmos-sdk/x/bank/types"
)
func queryState() error {
myAddress, err := sdk.AccAddressFromBech32("cosmos1...")
if err != nil {
return err
}
// Create a connection to the gRPC server.
grpcConn, err := grpc.Dial(
"127.0.0.1:9090", // your gRPC server address.
grpc.WithInsecure(), // The Cosmos SDK doesn't support any transport security mechanism.
// This instantiates a general gRPC codec which handles proto bytes. We pass in a nil interface registry
// if the request/response types contain interface instead of 'nil' you should pass the application specific codec.
grpc.WithDefaultCallOptions(grpc.ForceCodec(codec.NewProtoCodec(nil).GRPCCodec())),
)
if err != nil {
return err
}
defer grpcConn.Close()
// This creates a gRPC client to query the x/bank service.
bankClient := banktypes.NewQueryClient(grpcConn)
bankRes, err := bankClient.Balance(
context.Background(),
&banktypes.QueryBalanceRequest{Address: myAddress.String(), Denom: "atom"},
)
if err != nil {
return err
}
fmt.Println(bankRes.GetBalance()) // Prints the account balance
return nil
}
You can replace the query client (here we are using x/bank's) with one generated from any other Protobuf service. The list of all available gRPC query endpoints is coming soon.
Query for historical state using Go
Querying for historical blocks is done by adding the block height metadata in the gRPC request.
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"google.golang.org/grpc/metadata"
"github.com/cosmos/cosmos-sdk/codec"
sdk "github.com/cosmos/cosmos-sdk/types"
grpctypes "github.com/cosmos/cosmos-sdk/types/grpc"
banktypes "github.com/cosmos/cosmos-sdk/x/bank/types"
)
func queryState() error {
// --snip--
var header metadata.MD
bankRes, err = bankClient.Balance(
metadata.AppendToOutgoingContext(context.Background(), grpctypes.GRPCBlockHeightHeader, "12"), // Add metadata to request
&banktypes.QueryBalanceRequest{Address: myAddress.String(), Denom: "atom"},
grpc.Header(&header), // Retrieve header from response
)
if err != nil {
return err
}
blockHeight := header.Get(grpctypes.GRPCBlockHeightHeader)
fmt.Println(blockHeight) // Prints the block height (12)
return nil
}